How to Calculate Product Margin Percentage
Whether you are running a high-volume dropshipping store, a local boutique, or a growing SaaS company, the difference between success and bankruptcy often comes down to one single metric: your margin. It is not enough to just make sales; you need to make profitable sales. This is why learning how to calculate product margin percentage is arguably the most critical financial skill for any business owner in today’s competitive market.
Many entrepreneurs fall into the “revenue trap.” They see high sales numbers on their dashboard and assume the business is healthy. However, once they account for shipping, platform fees, returns, and marketing costs, they realize they are losing money on every transaction. Understanding your product margin percentage protects you from this disaster. It helps you set the right prices, cover your overheads, and scale your business sustainably without bleeding cash.
In this comprehensive guide, we will break down exactly how to calculate product margin percentage, the crucial difference between margin and markup, and how to use the calculator above to get instant, accurate results for your business.
If you want to skip the manual math and get straight to the numbers, simply scroll up and use our free Product Margin Percentage Calculator to analyze your profitability in seconds.
Product Margin Percentage Calculator
Product Margin Analysis
Generated on
Product Margin Percentage
| Cost Price (COGS) | - |
|---|---|
| Additional Costs/Fees | - |
| Net Profit | - |
- How to Calculate Product Margin Percentage
- What Is Product Margin Percentage?
- Product Margin Formula
- Step-by-Step: How to Calculate Product Margin Percentage
- Product Margin vs. Markup
- Real-World Examples
- How to Use our Product Margin Percentage Calculator
- Interpretation Guide: What Your Margin Percentage Means
- Industry Benchmarks
- Common Mistakes When Calculating Product Margin
- Related Calculators
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Summary
- Disclaimer
What Is Product Margin Percentage?
At its simplest, product margin percentage represents the portion of your selling price that is actual profit. It answers the vital question: “For every dollar (or rupee, pound, or yen) I make in sales, how many cents do I actually get to keep?”
It appears everywhere in business, from your quarterly financial reports to individual unit economics. Unlike revenue, which is often a vanity metric, margin is a sanity metric. You can have $1 million in revenue, but if your product margin is 1%, you are doing a massive amount of work for very little reward. While the currency may change, the concept is universal globally. Whether you are using US accounting standards (GAAP) or international principles (IFRS), knowing how to calculate product margin percentage ensures you are looking at the true health of your inventory rather than just top-line numbers. It serves as the ultimate “truth teller” for your pricing strategy.
Product Margin Formula
To perform a profit margin calculation, you need two key figures: your Selling Price (Revenue) and your Cost of Goods Sold (COGS).
Here are the standard formulas you need to know:
1. Margin Amount (Net Profit per Unit)
Margin Amount = Selling Price – Total Cost
2. Margin Percentage Formula
Margin Percentage = (Margin Amount ÷ Selling Price) × 100
3. Pricing for a Target Margin If you know your cost and want to hit a specific profit goal, use this to find your Selling Price:
Selling Price = Cost ÷ (1 – Target Margin %)
Step-by-Step: How to Calculate Product Margin Percentage
If you don’t have a product margin calculator handy, you can do this manually. However, precision is key. Let’s walk through the process in detail to ensure you get it right every time.
Step 1: Determine Your Total Cost (COGS)
This is where most errors happen. Your cost isn’t just the factory price. To accurately understand how to calculate product margin percentage, you must include the “landed cost.” This includes the manufacturing cost, shipping to your warehouse, customs duties, packaging materials, and any direct labor involved in prepping the item.
Step 2: Determine Your Selling Price
This is the final price the customer pays. Note: Do not include sales tax or VAT in this figure, as those are pass-through taxes collected for the government, not part of your revenue.
Step 3: Calculate the Profit
Subtract your Total Cost from your Selling Price.
Example: Selling Price $100 – Total Cost $60 = $40 Profit.
Step 4: Divide Profit by Selling Price
This is the step most people get wrong. You must divide by the Selling Price, not the Cost.
Example: $40 / $100 = 0.40
Step 5: Convert to Percentage
Multiply the result by 100 to get your final percentage.
Example: 0.40 × 100 = 40% Margin.
Warning: If you mistakenly divide your profit by your cost ($40 / $60), you get 66%. That is Markup, not Margin. Confusing these two figures can lead to dangerous pricing errors that erode your bottom line.
Product Margin vs. Markup
The terms “margin” and “markup” are often used interchangeably, but they result in very different numbers. According to Investopedia, while both analyze the same transaction, they show different perspectives: markup compares profit to cost, while margin compares profit to price.
Here is a quick breakdown to help you distinguish between them:
| Metric | Based On | Formula | Use Case |
| Margin | Selling Price | (Profit ÷ Selling Price) × 100 | Retail, Financial Reporting, Ecommerce |
| Markup | Cost Price | (Profit ÷ Cost) × 100 | Manufacturing, Wholesaling, Cost-Plus Pricing |
Real-World Examples
To fully understand how to calculate product margin percentage, it helps to look at distinct industry scenarios. Below is a detailed breakdown of how margins vary across different business models.
Industry Comparison Table
| Industry | Product | Total Cost | Selling Price | Profit | Margin % |
| Electronics | Bluetooth Speaker | $35.00 | $50.00 | $15.00 | 30% |
| Clothing | Denim Jacket | $20.00 | $80.00 | $60.00 | 75% |
| Grocery | Cereal Box | $3.80 | $4.00 | $0.20 | 5% |
| Dropshipping | Smart Watch | $20.00 | $30.00 | $10.00 | 33% |
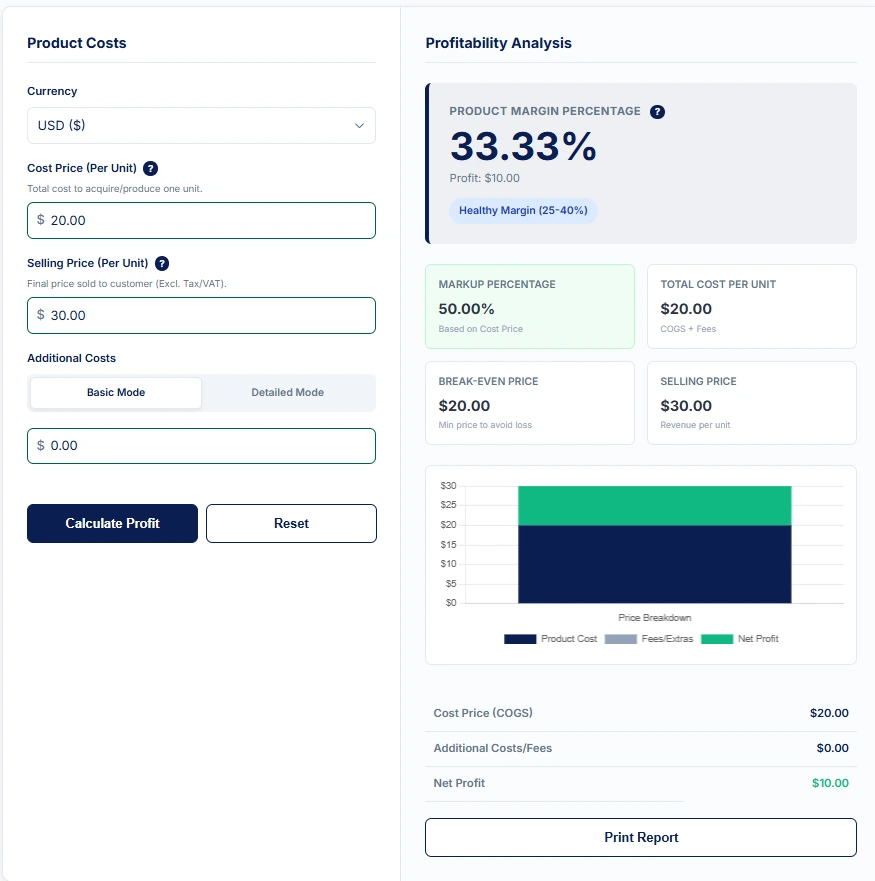
(Screenshot of calculator output)
Detailed Analysis
A. Electronics (High Risk, Competing on Specs)
In electronics, margins are often tighter due to high component costs.
- Verdict: A 30% margin is decent, but you need high sales volume to cover overheads like R&D and warranty returns.
B. Clothing (High Discounting)
Fashion has high initial margins (75%), but this is deceptive.
- Verdict: Clothing often requires heavy end-of-season discounting. That 75% margin might drop to 50% or lower once you account for sales events needed to move old stock.
C. Grocery (Low Margin, High Volume)
Grocery stores operate on razor-thin margins.
- Verdict: A 5% margin is typical. Profitability here depends entirely on inventory turnover—selling thousands of units quickly before they spoil.
D. Ecommerce / Dropshipping (Hidden Fees)
Dropshipping appears easy, but fees eat into profit.Verdict: A healthy ecommerce product margin usually sits around 30–40% after you deduct hidden costs like ad spend, Shopify fees, and payment gateway charges.
How to Use our Product Margin Percentage Calculator
We designed the calculator at the top of this page to be the easiest way to figure out your profitability without needing a spreadsheet. It handles complex scenarios, including platform fees for Amazon or Etsy sellers.
Here is a guide to the features:
1. Currency Selection
Start by choosing your currency (USD, EUR, GBP, INR, JPY). If you don’t see yours, simply select “No Currency” for a generic calculation.
2. Basic vs. Detailed Cost Modes
- Basic Mode: Perfect for a quick check. Enter your Unit Cost and Selling Price. You can add a single lump sum for “Additional Costs.”
- Detailed Mode (Recommended): Toggle this to break down hidden costs. You can input specific values for Shipping & Packaging, Platform Fees (like the 15% Amazon referral fee), and Payment Gateway Fees (like the 2.9% + 30% Stripe fee).
3. Interactive Analysis
Once you hit “Calculate Profit,” the tool doesn’t just give you a number. It generates:
- Profit Margin %: Your primary metric.
- Visual Badge: Tells you instantly if your margin is “Healthy,” “Thin,” or a “Loss.”
- Break-Even Price: The minimum price you can sell at without losing money.
- Dynamic Chart: A visual bar chart showing exactly where your money is going (Cost vs. Fees vs. Profit).
4. Printing Your Report
Need to show this to a business partner or save it for your records? Click the “Print Report” button. The calculator reformats into a clean, professional invoice-style document suitable for saving as a PDF or printing on paper.
Interpretation Guide: What Your Margin Percentage Means
You know how to calculate product margin percentage, but is your number actually good? Context is everything. A margin that is excellent for a grocery store would be disastrous for a software company.
Here is a general scale to help you interpret your results:
- 0% – 10% (Very Thin): Dangerously low. One small mistake in shipping or a slight supplier price hike puts you in the red. This is common in high-volume commodities or drop-servicing.
- 10% – 20% (Average): Standard for many physical retailers and big-box stores. You need tight inventory control here to succeed.
- 20% – 40% (Healthy): This is the sweet spot for most businesses. It provides a safety buffer for discounts, marketing errors, and unexpected cost increases.
- 40% – 60% (Excellent): Common in private label brands or specialty products where brand loyalty allows for higher pricing.
- 60%+ (Premium): Typical for luxury goods, digital products, or software where the cost of reproduction is near zero.
Industry Benchmarks
When asking “what is a good profit margin?”, the answer depends entirely on your industry. Compare your results against these standards:
- Retail (General): 20% – 40%
- Grocery / Supermarkets: 1% – 5% (Volume is king here)
- Consumer Electronics: 8% – 15% (Competition is fierce)
- Clothing & Apparel: 40% – 60% (To account for seasonal markdowns)
- Cosmetics: 60% – 80% (High branding costs)
- Jewelry: 40% – 70%
- SaaS / Digital Software: 70% – 90% (Zero reproduction cost)
Note: “Margins represent industry averages; actual results vary by brand, geography, and business model.”
Common Mistakes When Calculating Product Margin
Even experienced sellers make errors. When learning how to calculate product margin percentage, avoid these pitfalls:
- Confusing Cost and Price: If you divide profit by cost, you are calculating markup, not margin. This will artificially inflate your percentage and make you think you are more profitable than you actually are.
- Ignoring Variable Costs: If you only subtract the factory price of the item but forget the $5 shipping fee and the 3% credit card fee, your margin calculation is useless. Always use the “Detailed Mode” in our calculator to catch these.
- Forgetting Discounts: If your standard margin is 30%, but you run a “20% Off” sale, your profit doesn’t just drop by 20%—it might be wiped out entirely depending on your cost structure.
- Overlooking Returns: In ecommerce, a 5-10% return rate is common. If you don’t factor the cost of processing returns into your margin, your actual profit will be lower than calculated.
- Mixing Gross vs. Net: Gross margin usually looks at direct costs only. Net margin looks at all business expenses (rent, salaries). Be clear about which one you are calculating to avoid confusion.
Related Calculators
To get a full picture of your financial health, you should look beyond just product margin. Try our other tools:
- COGS Calculator: To accurately calculate your Cost of Goods Sold before using this tool.
- Operating Income Calculator: To see how your product margins translate to overall business profit.
- Inventory Turnover Ratio Calculator: To ensure your high-margin products aren’t just sitting on the shelf gathering dust.
Frequently Asked Questions
Summary
Understanding how to calculate product margin percentage is the foundation of a profitable business. It helps you price correctly, avoid losing money on hidden fees, and scale with confidence. Remember, high revenue is vanity, but high margin is sanity.
By mastering this calculation, you ensure that every sale contributes meaningfully to your business goals. Don’t leave your profitability to guesswork. Scroll up and use our Product Margin Percentage Calculator now to get instant clarity on your numbers.
Disclaimer
This article and the accompanying calculator are provided for informational and educational purposes only. They do not constitute professional financial, accounting, or legal advice. While every effort has been made to ensure accuracy, you should consult with a qualified accountant or financial advisor before making significant business pricing decisions.
